Reactive Logging With Spring WebFlux and Logstash

I have already introduced my Spring Boot library for synchronous HTTP request/response logging in one of my previous articles Logging with Spring Boot and Elastic Stack. This library is dedicated to synchronous REST applications built with Spring MVC and Spring Web. Since version 5.0 Spring Framework also offers support for reactive REST API through the Spring WebFlux project. I decided to extend support for logging in my library to reactive Spring WebFlux.
The repository with source code is available on GitHub: https://github.com/piomin/spring-boot-logging.git. It consists with two Maven modules: logstash-logging-spring-boot-starter for synchronous logging and reactive-logstash-logging-spring-boot-starter for reactive Spring WebFlux applications. The library is available on Maven Central:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.piomin</groupId>
<artifactId>reactive-logstash-logging-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
Motivations
Although we are working with reactive APIs and streams, a requirement for logging every incoming request and outgoing response is still actual. Today, we are usually running many, small applications communicating with each other, so we are focusing on storing the logs in a single, central place. Here comes Logstash and Elastic Stack. Spring Boot and Spring WebFlux allow you to build reactive microservices fast. My library takes care of gathering HTTP request/response logs, sending them to ELK with proper tags and correlation. Using it in your application does not require any additional source code. You just need to include the library.
However, some things need to be discussed when talking about reactive logging. Because we are logging full requests with payloads we need to buffer them. It somehow goes against the reactive programming, since we’re trying there to be efficient with the available resources. Also, integration with Logstash is realized synchronously. It is worth keeping those two things in mind when using reactive-logstash-logging-spring-boot-starter in your application.
Implementation Details
Spring WebFlux Dependencies
Since the library is used for Spring Boot reactive APIs logging it needs to have Spring WebFlux in the dependencies. In turn, Spring WebFlux is built on top of Project Reactor, so reactor-core artifact also has to be on the dependencies list. We also need some standard Spring libraries, used for example to provide auto-configuration.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webflux</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>${spring.boot.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId>
<artifactId>reactor-core</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0.RELEASE</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
Spring WebFlux Reactive Interceptor
With Spring WebFlux we don’t have popular Spring MVC components for caching request/response bodies: ContentCachingRequestWrapper and ContentCachingResponseWrapper. However, an approach will be pretty similar to the approach applied when building a library for synchronous logging. We need to access the request and response body by wrapping it and buffering without consuming the stream. To do that we first need to create classes extending ServerHttpRequestDecorator and ServerHttpResponseDecorator. They give us access to the message body while Spring WebFlux is reading the stream and writing to the stream.
When extending ServerHttpRequestDecorator we need to override getBody. Keep in mind that we cannot block a reactive stream, so one of doOn is suitable for accessing it. The body is published as Flux containing DataBuffer objects. Inside the asynchronous doOnNext method we write the buffer to the temporary byte array.
public class RequestLoggingInterceptor extends ServerHttpRequestDecorator {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RequestLoggingInterceptor.class);
public RequestLoggingInterceptor(ServerHttpRequest delegate) {
super(delegate);
}
@Override
public Flux<DataBuffer> getBody() {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
return super.getBody().doOnNext(dataBuffer -> {
try {
Channels.newChannel(baos).write(dataBuffer.asByteBuffer().asReadOnlyBuffer());
String body = IOUtils.toString(baos.toByteArray(), "UTF-8");
LOGGER.info("Request: method={}, uri={}, payload={}, audit={}", getDelegate().getMethod(),
getDelegate().getPath(), body, value("audit", true));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
When extending ServerHttpResponseDecorator we need to override writeWith method responsible for writing body to output reactive stream. We will listen for body writing events in doOnNext. Then we access DataBuffer and buffer it in ByteArrayOutputStream.
public class ResponseLoggingInterceptor extends ServerHttpResponseDecorator {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ResponseLoggingInterceptor.class);
private long startTime;
private boolean logHeaders;
public ResponseLoggingInterceptor(ServerHttpResponse delegate, long startTime, boolean logHeaders) {
super(delegate);
this.startTime = startTime;
this.logHeaders = logHeaders;
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> writeWith(Publisher<? extends DataBuffer> body) {
Flux<DataBuffer> buffer = Flux.from(body);
return super.writeWith(buffer.doOnNext(dataBuffer -> {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
Channels.newChannel(baos).write(dataBuffer.asByteBuffer().asReadOnlyBuffer());
String bodyRes = IOUtils.toString(baos.toByteArray(), "UTF-8");
if (logHeaders)
LOGGER.info("Response({} ms): status={}, payload={}, audit={}", value("X-Response-Time", System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime),
value("X-Response-Status", getStatusCode().value()), bodyRes, value("audit", true));
else
LOGGER.info("Response({} ms): status={}, payload={}, audit={}", value("X-Response-Time", System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime),
value("X-Response-Status", getStatusCode().value()), bodyRes, value("audit", true));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}));
}
}
Spring WebFlux Logging Filter
To be able to decorate requests and responses we first need to declare filter intercepting an incoming request. To do that we have to declare a bean that implements WebFilter and its method filter(...). The filtering method allows you to access the exchange object, which contains objects representing request and response. So if we would like to decorate request and response objects we first need to decorate ServerWebExchange. We may easily do it by defining an instance of the ServerWebExchangeDecorator object with overridden methods getRequest and getResponse. Our decorators are responsible just for listening to events related to message body processing. So, the significant information here is that if a message has an empty body, the listening methods won’t be fired. That’s why I decided to add a code for analyzing the length of content to log a request or response message with an empty body. It is based on the HTTP header Content-Length.
public class ReactiveSpringLoggingFilter implements WebFilter {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ReactiveSpringLoggingFilter.class);
private UniqueIDGenerator generator;
private String ignorePatterns;
private boolean logHeaders;
private boolean useContentLength;
public ReactiveSpringLoggingFilter(UniqueIDGenerator generator, String ignorePatterns, boolean logHeaders, boolean useContentLength) {
this.generator = generator;
this.ignorePatterns = ignorePatterns;
this.logHeaders = logHeaders;
this.useContentLength = useContentLength;
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, WebFilterChain chain) {
if (ignorePatterns != null && exchange.getRequest().getURI().getPath().matches(ignorePatterns)) {
return chain.filter(exchange);
} else {
generator.generateAndSetMDC(exchange.getRequest());
final long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> header = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders().get("Content-Length");
if (useContentLength && (header == null || header.get(0).equals("0"))) {
if (logHeaders)
LOGGER.info("Request: method={}, uri={}, headers={}, audit={}", exchange.getRequest().getMethod(),
exchange.getRequest().getURI().getPath(), exchange.getRequest().getHeaders(), value("audit", true));
else
LOGGER.info("Request: method={}, uri={}, audit={}", exchange.getRequest().getMethod(),
exchange.getRequest().getURI().getPath(), value("audit", true));
}
ServerWebExchangeDecorator exchangeDecorator = new ServerWebExchangeDecorator(exchange) {
@Override
public ServerHttpRequest getRequest() {
return new RequestLoggingInterceptor(super.getRequest(), logHeaders);
}
@Override
public ServerHttpResponse getResponse() {
return new ResponseLoggingInterceptor(super.getResponse(), startTime, logHeaders);
}
};
return chain.filter(exchangeDecorator)
.doOnSuccess(aVoid -> {
logResponse(startTime, exchangeDecorator.getResponse(), exchangeDecorator.getResponse().getStatusCode().value());
})
.doOnError(throwable -> {
logResponse(startTime, exchangeDecorator.getResponse(), 500);
});
}
}
}
The last step of implementation is auto-configuration. Here’s the class responsible for it.
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "logging.logstash")
public class ReactiveSpringLoggingAutoConfiguration {
private static final String LOGSTASH_APPENDER_NAME = "LOGSTASH";
private String url = "localhost:8500";
private String ignorePatterns;
private boolean logHeaders;
private boolean useContentLength;
private String trustStoreLocation;
private String trustStorePassword;
@Value("${spring.application.name:-}")
String name;
@Bean
public UniqueIDGenerator generator() {
return new UniqueIDGenerator();
}
@Bean
public ReactiveSpringLoggingFilter reactiveSpringLoggingFilter() {
return new ReactiveSpringLoggingFilter(generator(), ignorePatterns, logHeaders, useContentLength);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty("logging.logstash.enabled")
public LogstashTcpSocketAppender logstashAppender() {
...
}
}
Usage of Spring WebFlux Logging
To be able to create reactive APIs with Spring Boot we first need to include Spring WebFlux starter to Maven dependencies.
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>pl.piomin.test</groupId>
<artifactId>sample-webflux-app</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.piomin</groupId>
<artifactId>reactive-logstash-logging-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
I have already described how to build microservices architecture with Spring WebFlux and Spring Cloud in one of my previous articles Reactive Microservices with Spring WebFlux and Spring Cloud. So for more information about advanced use cases, you can refer to this article. Here’s a typical controller implementation with Spring WebFlux Mono and Flux objects.
@RestController
public class AccountController {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AccountController.class);
@Autowired
private AccountRepository repository;
@GetMapping("/customer/{customer}")
public Flux<Account> findByCustomer(@PathVariable("customer") String customerId) {
LOGGER.info("findByCustomer: customerId={}", customerId);
return repository.findByCustomerId(customerId);
}
@GetMapping
public Flux<Account> findAll() {
LOGGER.info("findAll");
return repository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Mono<Account> findById(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
LOGGER.info("findById: id={}", id);
return repository.findById(id);
}
@PostMapping
public Mono<Account> create(@RequestBody Account account) {
LOGGER.info("create: {}", account);
return repository.save(account);
}
}
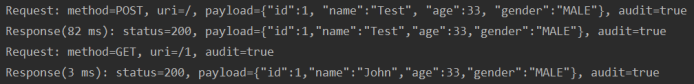
Here are the log entries for GET (empty body) and POST requests.
We can customize the library behaviour by overriding default values of configuration properties with logging.logstash.*. Here’s the typical configuration that enables embedded Logstash appender configuration, changes default Logstash URL, includes list of headers to the log and ignores logging of /favicon.ico requests.
logging.logstash:
enabled: true
url: 192.168.99.100:8500
ignorePatterns: .*(favicon).*
logHeaders: true
With the settings visible above the logs are sent to Logstash available on address 192.168.99.100:8500.
Summary
Spring Boot Logging library now supports logging for synchronous HTTP API with Spring MVC and reactive HTTP API with Spring WebFlux. The detailed description of the libraries configuration features may be found in my article Using logstash-logging-spring-boot-starter for logging with Spring Boot and Logstash. You can report the bugs or propose new enhancements here: https://github.com/piomin/spring-boot-logging/issues. Any feedback would be very welcome.
12 COMMENTS